1.Surface shape
2. Curvature test
3. Surface flatness or surface roughness
4. Is the surface on both sides of the glass flat enough?
5. Angle test, some optical components are angled, which can be used to measure the accuracy
6. Stress tests, such as glasses or camera lenses, can test the amount of deformation of the glass when it must be clamped with other objects.
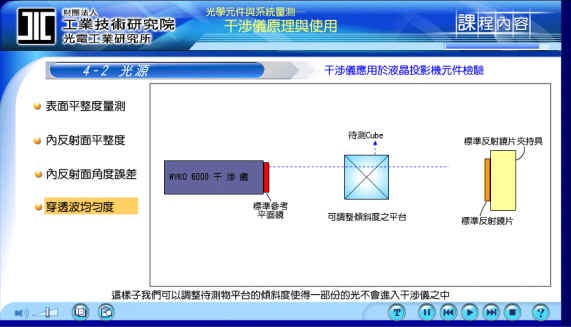
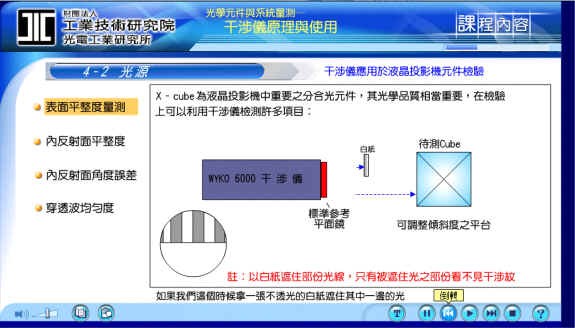
1 .Example Measuring surface flatness:
As shown in the following figure, when the light source is hit by the reference surface to the first surface of the object to be tested, we will see the difference between it and the surface flatness of the surface to be tested. It can be directly read by the computer. The correct data results. If we cover the light on one side with an opaque white paper, then the hidden part will no longer appear light from below, but only a part of the reflective stripes.
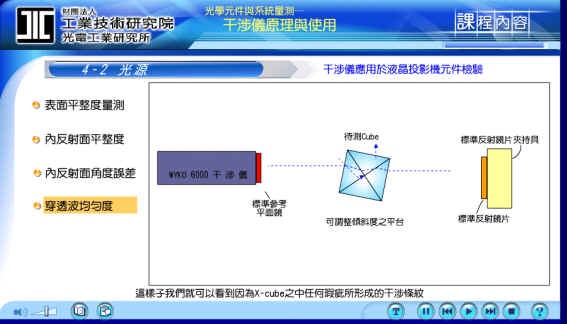
2.The flatness of the internal reflection surface:
The light source is reflected when the reference surface hits the first surface of the object to be tested, but can also be inserted into the object to be tested, and then reflected back to the reference surface through the reflection process, that is, the same structure can be used to measure the object. On both sides, do you know which surface we are measuring? If we cover the light on one side with an opaque white paper, then the hidden part will no longer appear from below. , but it will show part of the reflection stripe that is not covered, then the surface flatness is measured. The light source of internal reflection is driven into the object to be tested from above, and then comes out from below through reflection, so if we take An opaque white paper covers the light above, then there will be no more light coming out from below, so that it is known that the current measurement is the flatness of the internal reflection surface.
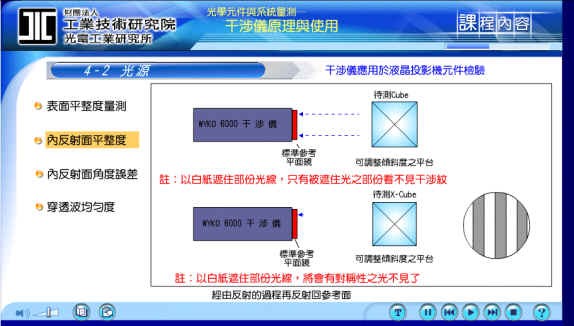
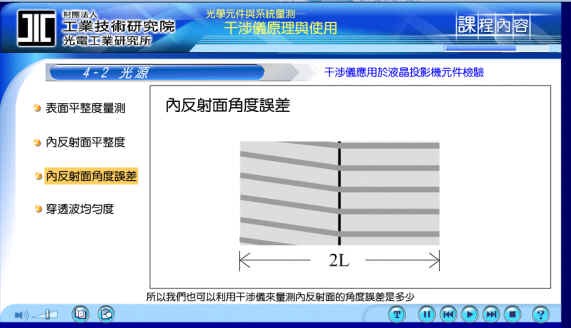
3. Measure the angular error of the internal reflection surface:
This is a side view of the X-cube. In theory, we will try to reach nearly 90 degrees, so we can also use an interferometer to measure the angular error of the internal reflection surface.
4 Measure the flatness of the penetrating wavefront:
Light must be penetrated in the projector. If the X-cube has some flaws, the displayed image will be not beautiful, so the flatness of the penetrating wave must be measured.
When the light source is struck from above, when it hits the standard reflective lens through the object to be tested, it is reflected back. If the position of the object to be tested is flat, then each light will be reflected back in the original way, and may be divided. It is clear which interference surface is generated by the interference fringe. At this time, the inclination of the platform to be tested can be adjusted so that part of the light does not enter the interferometer, so the interference fringes can be clearly seen.